Heterogeneous catalyst is composed of a major active component, the proportion of which surpasses that of other components, and secondary components, which are included to improve catalystHeterogeneous catalysts are catalysts which exist in a different phase to the reactants For example, a solid catalyst used in a reaction with liquids would be a heterogeneous catalyst – you can remember this by knowing that 'hetero' means 'different'Learn the definition of 'heterogeneous catalyst' Check out the pronunciation, synonyms and grammar Browse the use examples 'heterogeneous catalyst' in the great English corpus
Heterogeneous Catalysis Surface Chemistry Catalysis Group Ppt Download
How does a heterogeneous catalyst work
How does a heterogeneous catalyst work-Homogeneous catalysts are those which exist in the same phase (gas or liquid) as the reactants, while heterogeneous catalysts are not in the same phase as the reactants Typically, heterogeneous catalysis involves the use of solid catalysts placed in a liquid reaction mixture Catalysis Note the lowered activation energy of the catalyzed pathway The reaction between acid and metal is a heterogeneous reaction A reaction between a gas and a liquid, as between air and seawater, is heterogeneous A reaction at the surface of a catalyst is heterogeneous In contrast, a reaction between two miscible liquids or between two gases is homogeneous




Catalysts Definition Types Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Difference Between Homogeneous Catalysis and Heterogeneous Catalysis Video Lecture from Surface Chemistry Chapter of Chemistry Class 11 for HSC, IIT JEE, CBSIn catalysis Heterogeneous catalysis Many catalytic processes are known in which the catalyst and the reactants are not present in the same phase—that is, state of matter These are known as heterogeneous catalytic reactions They includeSubject Chemistry Adsorption theory This theory can be applied to heterogeneous catalysis only As the name suggests the reactant is adsorbed on the surface of the catalyst and the effective concentration of the reactant is generally increased on the surface, the reactants are brought closer and the reaction speed is increased
Computational efforts in heterogeneous catalysis are constantly striving towards a better and more accurate understanding of chemical reactions at interfaces Simple energy relations based on bond order conservation principles are beginning to have a considerable impact on studies of catalytic reactivity and a new era of theorydriven catalyst designA contactcatalyst Search the Dictionary for The basic answer is that heterogeneous catalysis "in the gas phase" just means that the materials being reacted are gases They catalysts can be liquids or solids (more common) A simple, but very, very important example is the reaction used to convert ammonia into nitric acid (vital for fertiliser production, important for many organic
Definition of heterogeneous catalyst 1) A catalyst that exists in a different phase (solid, liquid or gas) from the reactants;Heterogeneous catalysts are chemical catalysts whose physical phase is different from the physical phase of the reactants and/or products that take part in the catalyzed chemical reaction Typically, solid phase heterogeneous catalysts are employed in order to facilitate the chemical reaction between two gaseous reactantsHeterogeneous catalysts are catalytic compounds that are in a contradictory phase from that of the phase of the reaction combination Heterogeneous catalysis is found in the liquid phase, gas phase, and solid phase Operative temperature for heterogeneous catalysis is harsh as compared to the homogeneous process



Combining Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Catalysis Feature Chemistry World



Catalyst Facts Summary Definition Chemistry Revision
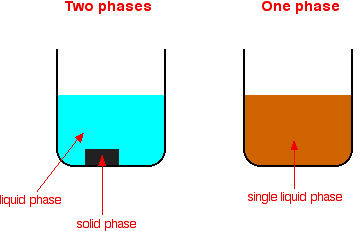
The difference between heterogeneous and homogeneous mixtures is the degree to which the materials are mixed together and the uniformity of their composition A homogeneous mixture is a mixture in which the components that make up the mixture are uniformly distributed throughout the mixture The composition of the mixture is the same throughoutHeterogeneous catalysis involves systems in which the reaction takes place in different phases The word "phase" here refers to solid, liquid, gas, or immiscible liquids like oil and water Generally the catalyst is in the solid phase, and the reactants are gases or liquidsHeterogeneous Catalyst Heterogeneous catalysts are certain particulate solids of high surface area (1–300m2 g−1) that increase the rates of attaining equilibria From Encyclopedia of Separation Science, 00 Related terms Catalysis;




Combining Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Catalysis Feature Chemistry World




Heterogeneous Homogeneous Catalysts Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Normally the catalyst is a solid and the reactants are gas or liquid; Contents1 Catalysis2 Promoters and Poisons3 Classification of Catalysts31 1 Homogeneous catalysts4 Mechanism of Homogeneous Catalytic Reactions41 Heterogeneous Catalysts Catalysis A substance which increases the speed of a reaction without being consumed in the reaction is called a catalyst The phenomenon of increasing the rate of reaction by the use of catalyst is called catalysisA contact catalyst Was this definition helpful?




Machine Learning For Heterogeneous Catalyst Design And Discovery Goldsmith 18 Aiche Journal Wiley Online Library



Q Tbn And9gctrvbbisy7ikjyh35 8msk3jkudkzizuszlwrim5fn3f2i54ygk Usqp Cau
Heterogeneous catalysis This involves the use of a catalyst in a different phase from the reactants Typical examples involve a solidcatalyst with the reactants as either liquids or gases Note It is important that you remember the difference between theHeterogeneous Catalysis Wednesday, Catalyst Definition?The catalyst is not behaving like a conventional homogeneous molecular catalyst but more like the metallic active sites exploited in heterogeneous catalysts 'We still get singlesite




Catalysis Mechanism Types Enzymes Biocatalysts Videos Examples




Principles And Practice Of Heterogeneous Catalysis 2nd Edition Wiley
This video has been updated Watch the complete and newest version here https//wwwyoutubecom/watch?v=xhGfFtn0XugIn this video we'll be introducedStart studying Chemistry Catalysts Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study toolsWhat Do yuo know about Chemistry # posted by Dr Abd El Rahman Salah @ 3 AM 1 comments About Me Name Dr Abd El Rahman Salah View my complete profile Links



Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Catalytic Reduction Of Amides And Related Compounds Using Molecular Hydrogen Nature Communications




Heterogeneous Catalysis Alchetron The Free Social Encyclopedia
UNESCO – EOLSS SAMPLE CHAPTERS INORGANIC AND BIOINORGANIC CHEMISTRY – Vol II Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Catalysis Erica Farnetti, Roberta Di Monte and Jan Kašpar ©Encyclopedia of Life Support Systems (EOLSS) terms ab,, and cd,, represent the stoichiometric coefficients of the reactionFor such a reaction we can define the reaction rate asCatalyst Definition Chemistry Software AMD Catalyst Software Suite for Windows Vista/7 32bit v114 This release of ATI Catalyst™ provides full OpenGL™ 30 extension support Heterogeneous Catalysts When the catalyst is in different phase than the reactants, it is called heterogeneous catalyst Such reactions are called heterogeneous catalytic reactions In heterogeneous catalysis, catalyst is generally a solid and the reactants are generally gases
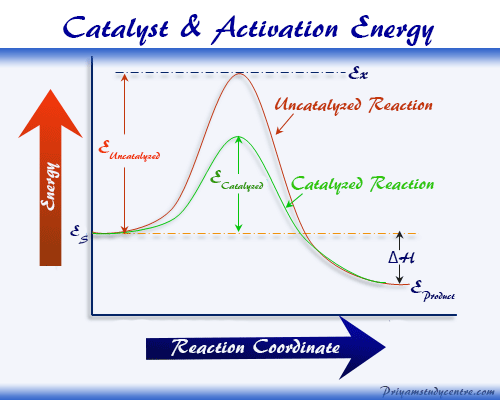



Chemical Catalyst Definition Reaction Types And Examples




Pdf Major Advances And Challenges In Heterogeneous Catalysis For Environmental Applications A Review
Noun heterogeneous catalysis (chemistry) Catalysis in which the catalyst is present in a separate phase; A homogeneous catalyst is a catalyst that is capable of dissolving in solution, because it by definition is in the same phase as the rest of the reactants in the solution Here are the principles of homogeneous catalysts that I see in my textbook (Inorganic Chemistry, Shriver, Atkins, Ch 25) PROS Homogeneous catalysts are effective at being highly selective towardsNoun heterogeneous catalysis Heterogeneous catalysis is catalysis in which the catalyst does not take part in the reaction that it increases 0;




Pdf Heterogeneous Catalyst Deactivation And Regeneration A Review Semantic Scholar




Heterogeneous Catalysis Wikipedia
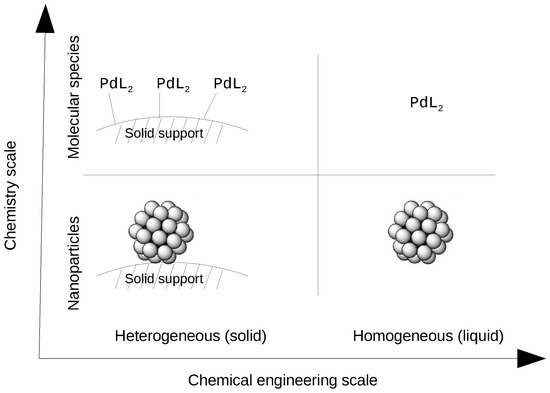
A heterogeneous catalysis is one where the reaction components are not in the same phase Enzymes and other biocatalysts are often considered as a third category Similar mechanistic principles apply to heterogeneous, homogeneous, and biocatalysis Heterogeneous catalysisChemical Catalysis Catalytic research at Texas A&M University covers a broad range of homogeneous catalysis, heterogeneous catalysis, and biocatalysis Many of the important challenges in modern catalysis research are under investigation at TAMU, including photo and electrochemical production of renewable energy, the efficient conversion of Heterogeneous Catalysis if the catalyst is present in a different phase than that of reactants, it is called a Heterogeneous catalyst and this type of catalysis is known as Heterogeneous Catalysis Ex Manufacture of ammonia from N 2 and H 2 by Haber's process using iron as catalyst (ii) Manfacture of sulphuric acid by oxidation of SO 2 to
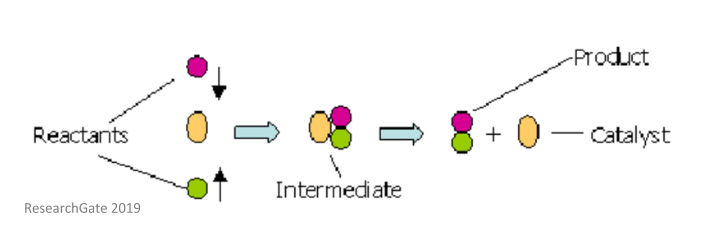



Catalyst Facts Summary Definition Chemistry Revision




Heterogeneous Catalysis Wikipedia
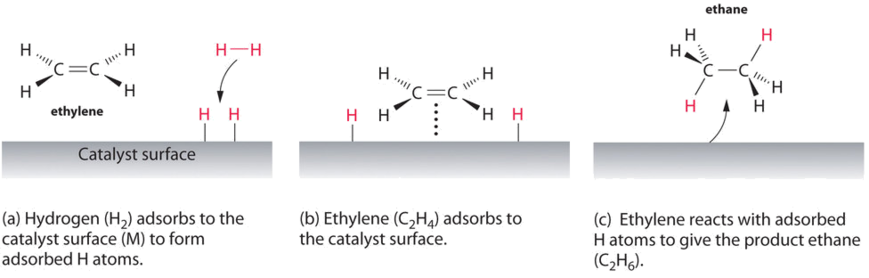
The catalyst whose phase differs from that of the reactants in the reaction is called heterogeneous catalyst and this type of catalysis process is called heterogeneous catalysis Examples of Heterogeneous Catalysis and Catalysts – 1Heterogeneous Catalysis Explanation Heterogeneous catalysis is a type of catalysis in which the catalyst occupies a different phase from the reactants and products Heterogeneous catalysts can be more easily recycled than homogeneous, but it is more difficult to characterize the catalyst and optimize propertiesIn general, heterogeneous catalysts are solids that are added into gas or liquid reaction mixtures In heterogeneous catalysis, the reactants adsorb onto binding sites on the surface of the catalyst, and the availability of these reaction sites can limit the rate of heterogeneous reactions




Auliya Rahman Ppt Cbr Heterogeneous Catalysis Catalysis




Catalysis Fundamentals Chemical Engineering Page 1
A catalyst is a compound used to help a reaction occur faster by lowering the activation energy There are two types of catalysts, homogeneous and heterogeneous A homogeneous catalyst is aIt proceeds by the reaction of chemisorbed complexesHow to Cite Ollis, D F and Pruden, A L (19) Photoassisted Heterogeneous Catalysis Definition and Hydrocarbon and Chlorocarbon Oxidations, in Heterogeneous
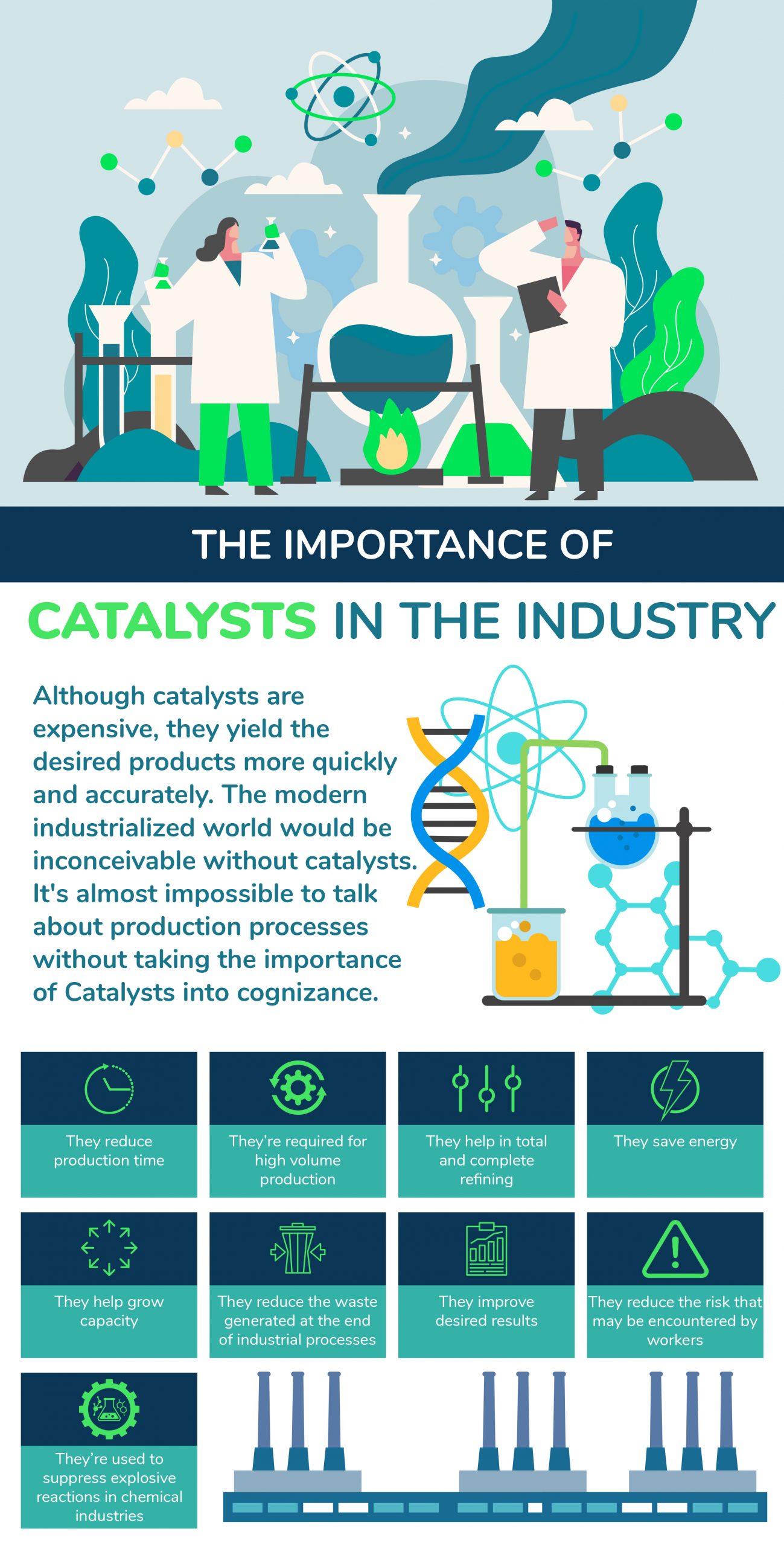



What Are Industrial Catalysts Recognized Trading Shipping Inc




Give Four Examples Of Heterogeneous Catalytic Reactions Youtube
Chemistry Dictionary Definition of heterogeneous catalyst A catalystthat exists in a different phase (solid, liquidor gas) from the reactants;Heterogeneous catalysis In chemistry, heterogeneous catalysis is catalysis where the phase of catalysts differs from that of the reactants or products The process contrasts with homogeneous catalysis where the reactants, products and catalyst exist in the same phase Phase distinguishes between not only solid, liquid, and gas components, but also# posted by Dr Abd El Rahman Salah @ 845 AM 0 comments Welcome to chemistry life What is Chemistry?




Heterogeneous Catalysis Surface Chemistry Catalysis Group Ppt Download
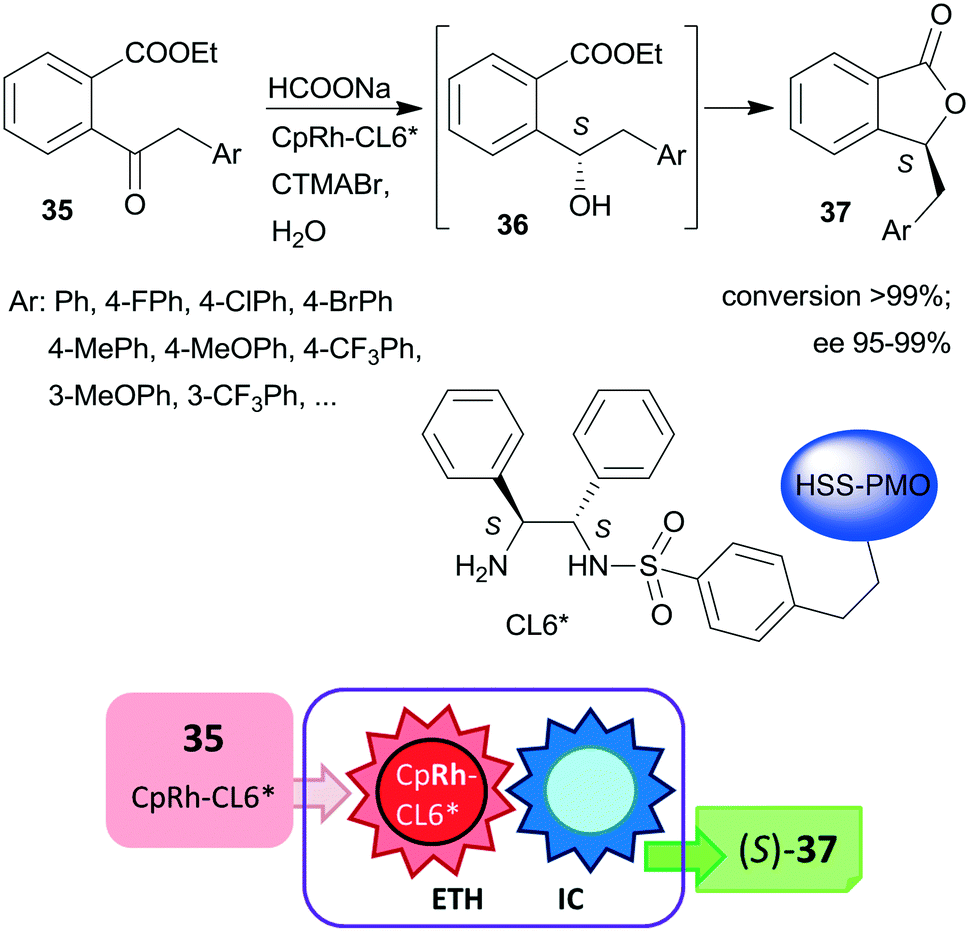



Asymmetric One Pot Reactions Using Heterogeneous Chemical Catalysis Recent Steps Towards Sustainable Processes Catalysis Science Technology Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 C7cya
Catalyst Definition Chemistry, free catalyst definition chemistry software downloads, Page 2Catalysts are substances which alters the rate of reaction by changing the path of reaction The reaction which involves a catalyst in their system are known as a catalytic reaction and the phenomenon is called catalysisJournal of Molecular Catalysis 1986, 37 (23) , 10 DOI /(86)8500 R L AUGUSTINE, F YAGHMAIE, J F VAN PEPPEN ChemInform Abstract HETEROGENEOUS CATALYSIS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 2 A MECHANISTIC COMPARISON OF NOBLEMETAL CATALYSTS IN OLEFIN HYDROGENATION



Types Of Catalysis



How Do Catalysts Work
Catalyst (chemistry) a substance that initiates or accelerates a chemical reaction without itself being affected accelerator chemical science , chemistry the science of matter;(Chemical Engineering General) Heterogeneous catalysis is catalysis in which the catalyst does not take part in the reaction that it increases With heterogeneous catalysis, the catalyst and the reactants may be in different phases, for example gasphased reactions which are In heterogeneous catalysis, catalysts provide a surface to which reactants bind in a process of adsorption In homogeneous catalysis, catalysts are in the same phase as the reactants Enzymes are biological catalysts that produce large increases in reaction rates and tend to be specific for certain reactants and products



Heterogenous Catalysis Chemistry Is Love



14 7 Catalysis Chemistry Libretexts
4 Heterogeneous involves more than one phase usually the catalyst is a solid and the reactants and products are in liquid or gaseous form A heterogeneous catalytic reaction occurs at or very near the fluidsolid interface Reactions between gasesThe branch of the natural sciences dealing with the composition of substances and their properties and reactions As its name implies, a heterogeneous catalyst exists as a separate phase (almost always a solid) from the one (most commonly a gas) in which the reaction takes place The catalytic affect arises from disruption (often leading to dissociation) of the reactant molecules brought about by their interaction with the surface of the catalyst




Heterogeneous Catalyst An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Catalysts Definition Types Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Understanding Chemistry CATALYSIS MENU An introduction to types of catalysis Explains the difference between heterogeneous and homogeneous catalysis with examples of each (Heterogeneous hydrogenation of carboncarbon double bonds, catalytic converters, vanadium(V) oxide in the Contact ProcessWhile the term "heterogeneous mixture" sounds like it could be a complicated concept, in reality, it is actually quite simple A mixture is made up of two or more substances, and in a heterogeneous mixture, those substances are not uniformly distributed, meaning that the substances that make up the mixture can be distinguished from one another upon examination



Catalysts Free Full Text About Solid Phase Vs Liquid Phase In Suzuki Miyaura Reaction Html
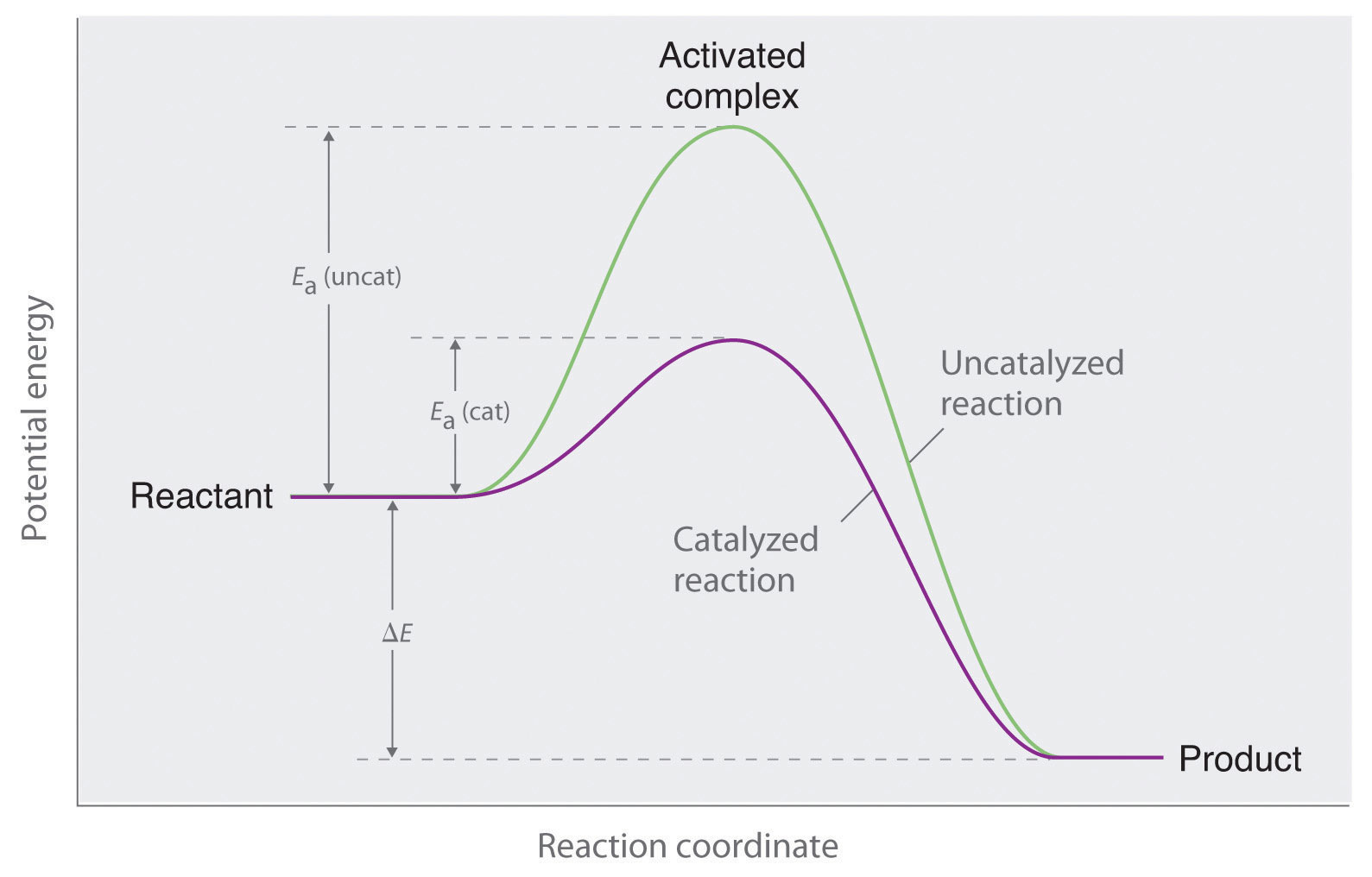



Catalysis




Difference Between Homogeneous Catalysis And Heterogeneous Catalysis Surface Chemistry Youtube
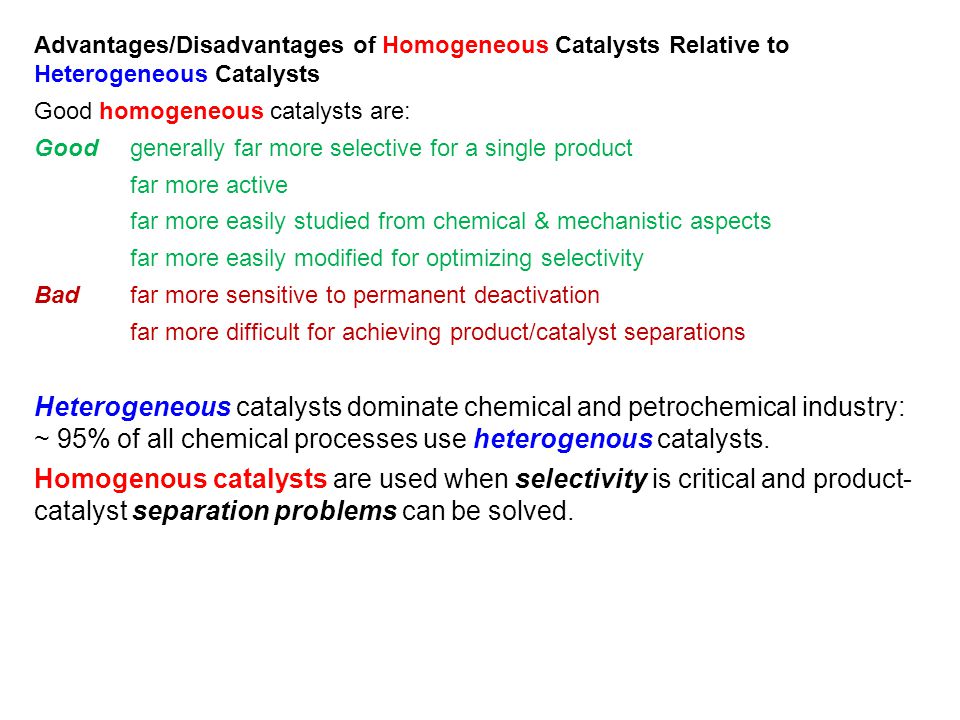



Homogeneous Catalysis Introduction Ppt Video Online Download



1




Catalysis Chemistry Classification Chemical Reactions Britannica




Heterogeneous Catalysis Wikipedia



Types Of Catalysis




The Societal Significance Of Catalysis And The Growing Practical Importance Of Single Site Heterogeneous Catalysts Proceedings Of The Royal Society A Mathematical Physical And Engineering Sciences




How To Measure The Reaction Performance Of Heterogeneous Catalytic Reactions Reliably Sciencedirect
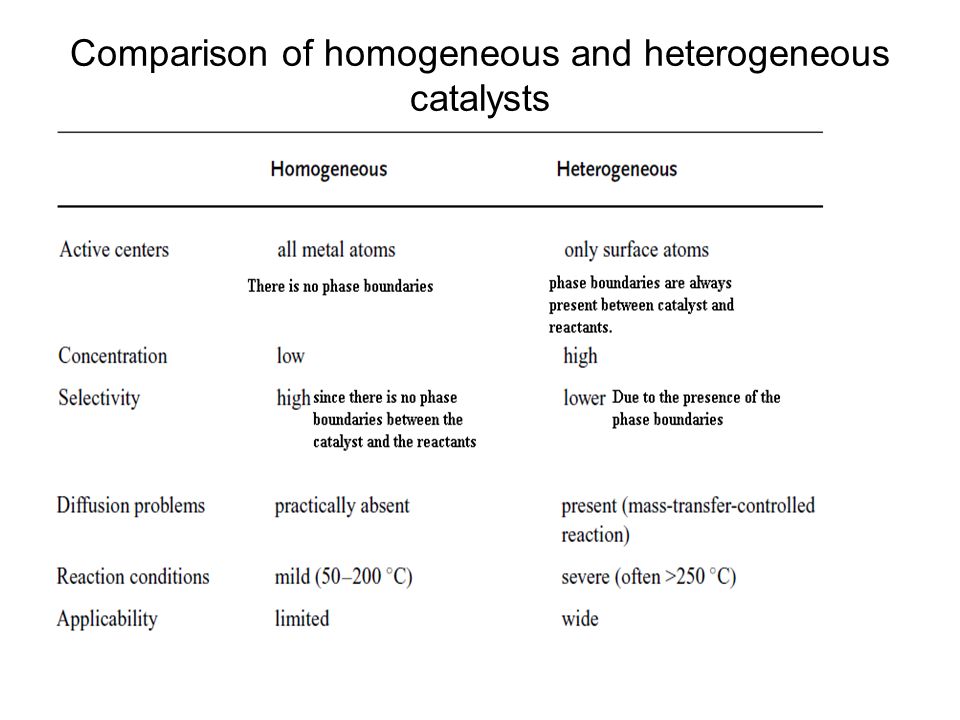



Heterogeneous Catalysis Ppt Video Online Download
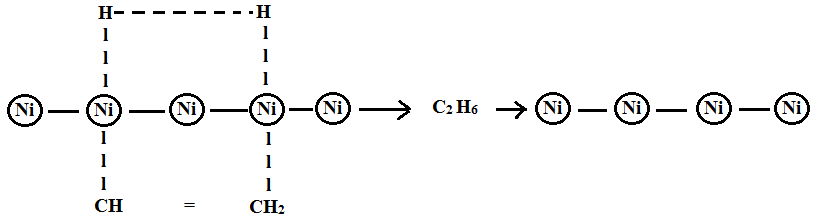



Catalyst Meaning Definition Mechanism Types Catalysis
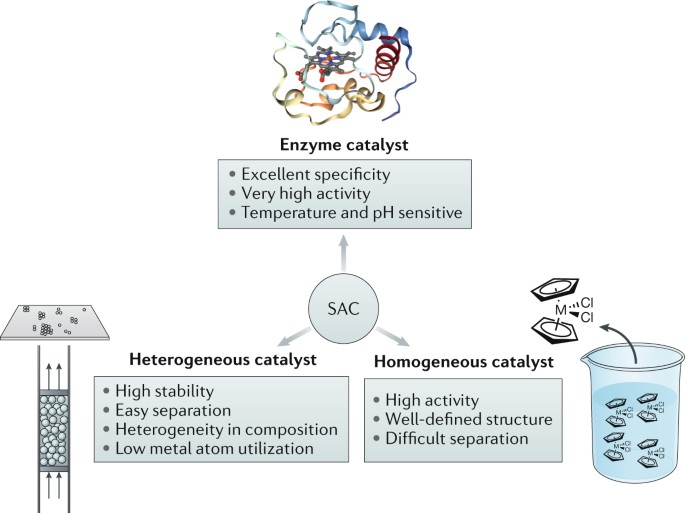



Heterogeneous Single Atom Catalysis Nature Reviews Chemistry




Rate Processes Catalysts Rate Processes In Chemical Reactions Kinetics And Equilibrium Mcat Content




Types Of Catalysts Article Kinetics Khan Academy
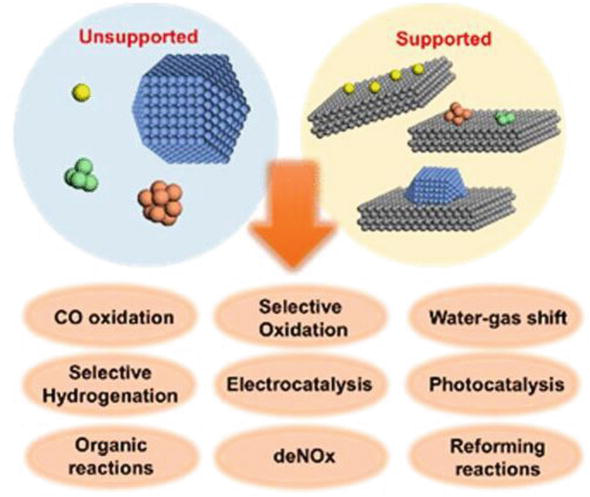



Heterogeneous Catalytic Process For Wastewater Treatment Intechopen
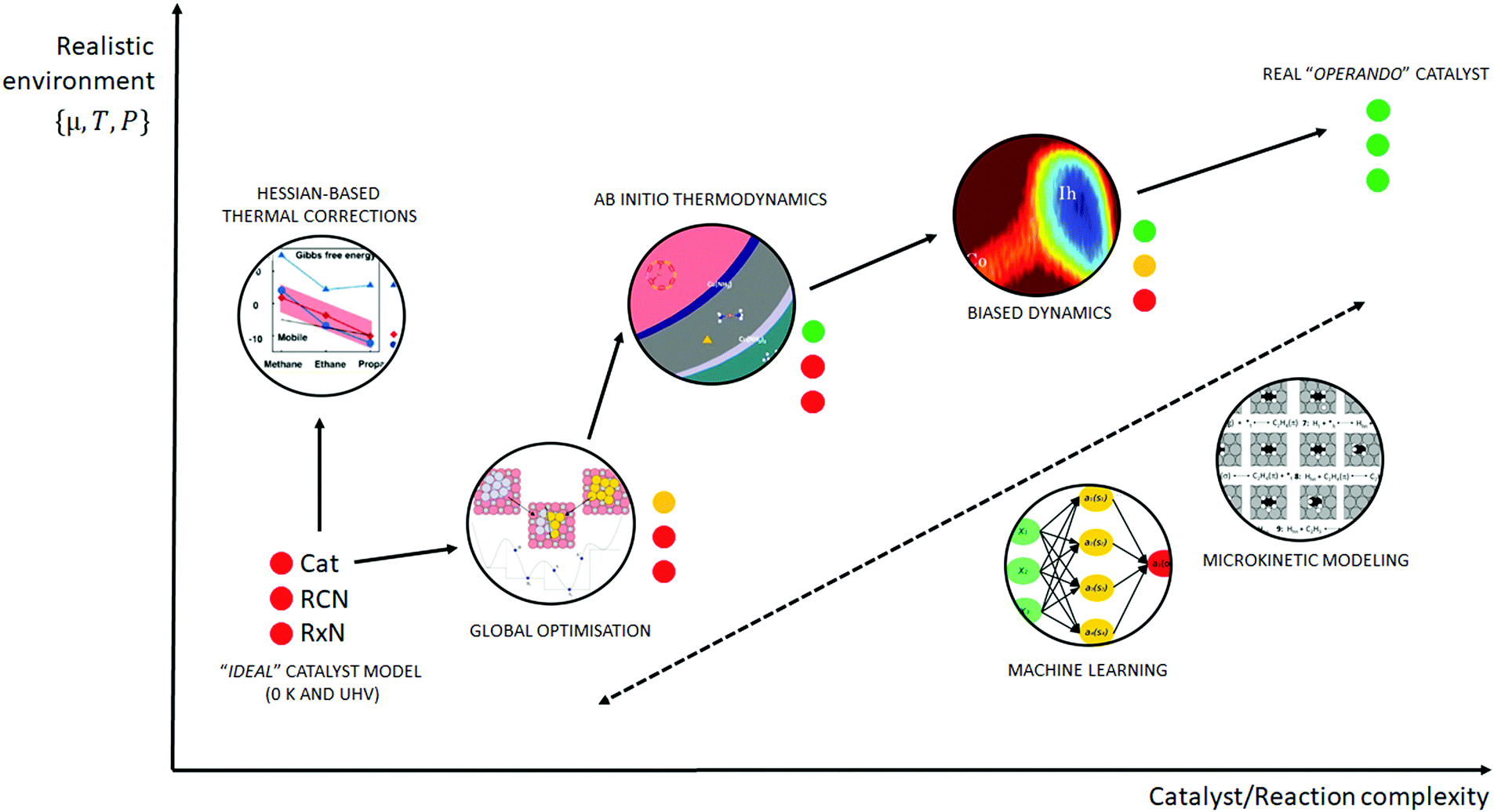



Towards Operando Computational Modeling In Heterogeneous Catalysis Chemical Society Reviews Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 C8csj



1
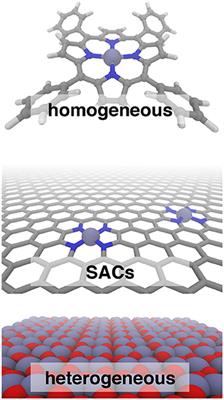



Frontiers Bridging The Homogeneous Heterogeneous Divide Modeling Spin For Reactivity In Single Atom Catalysis Chemistry




Explain The Difference Between A Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Catalyst Give An Example Of Each Youtube




Catalysis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Catalysis Heterogeneous Catalysis Britannica




Heterogeneous Catalytic Process For Wastewater Treatment Intechopen




Heterogenous Catalysis Chemistry Is Love



17 6 Catalysts And Catalysis Chemistry Libretexts




Catalyst Examples Types Function What Is A Catalyst Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Heterogeneous Catalysis All About Drugs
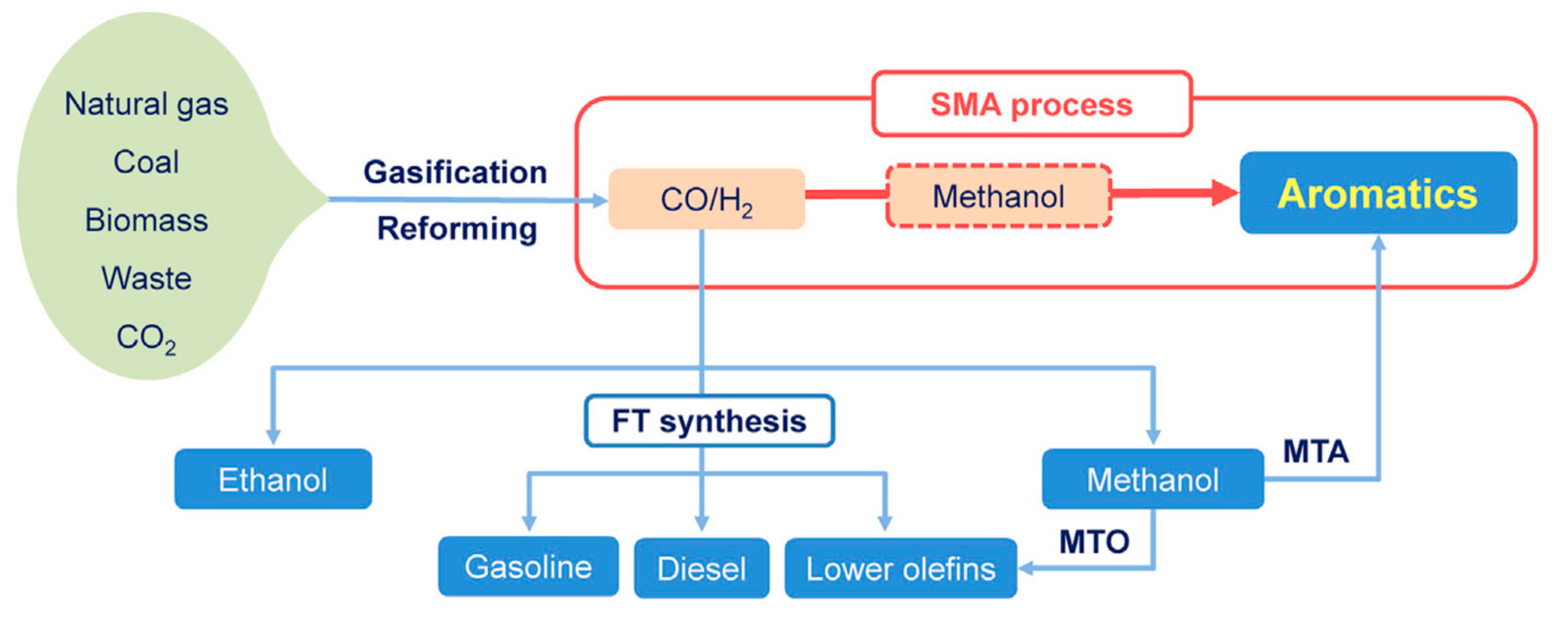



Catalysts Free Full Text Heterogeneous Catalysis On Metal Oxides Html




Neet Ug Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Catalyst In Hindi Offered By Unacademy




Principles Of Heterogeneous Catalysis Dumesic Major Reference Works Wiley Online Library
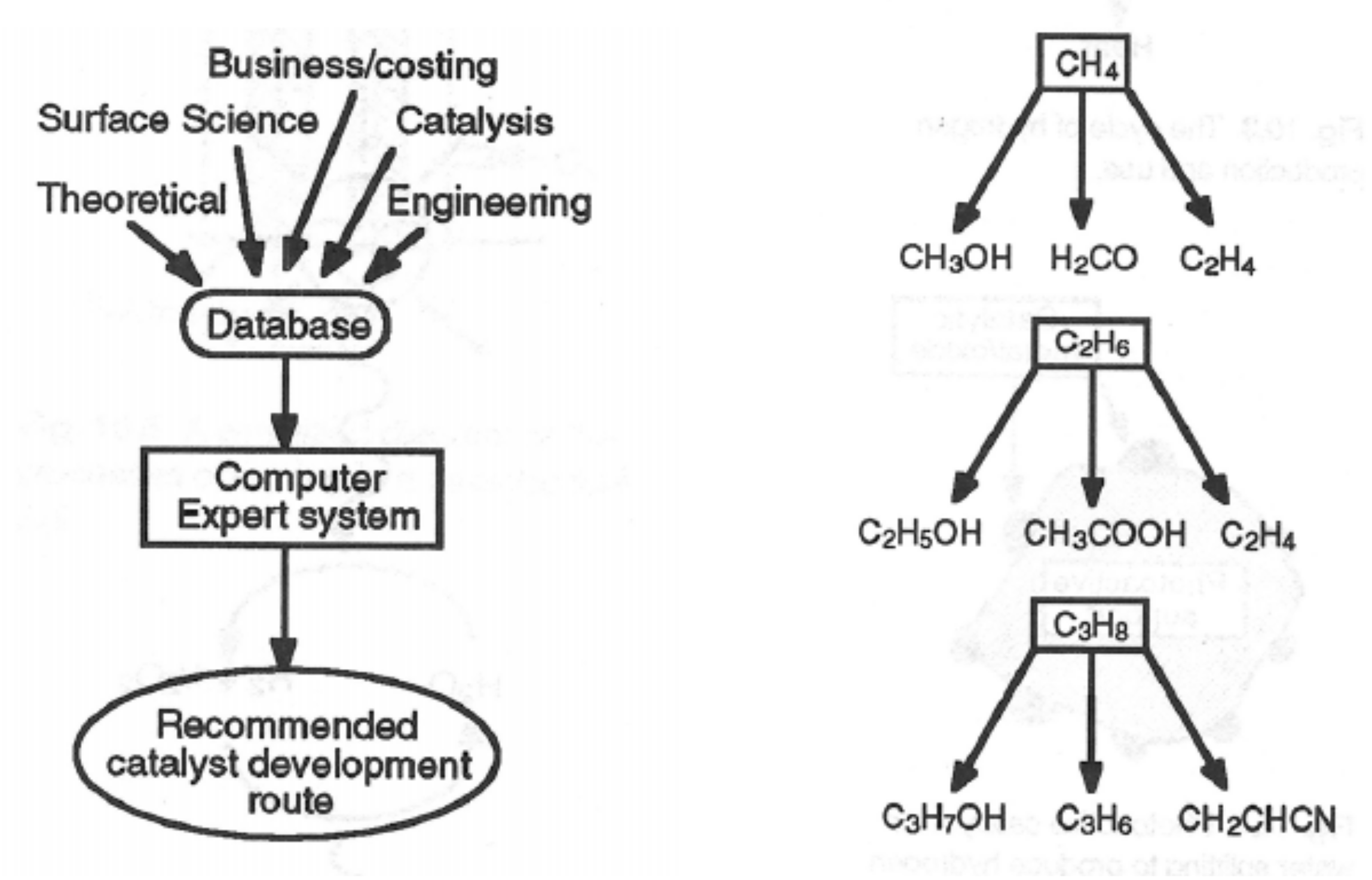



Catalysts Free Full Text Heterogeneous Catalysis On Metal Oxides Html




Pdf Major Advances And Challenges In Heterogeneous Catalysis For Environmental Applications A Review
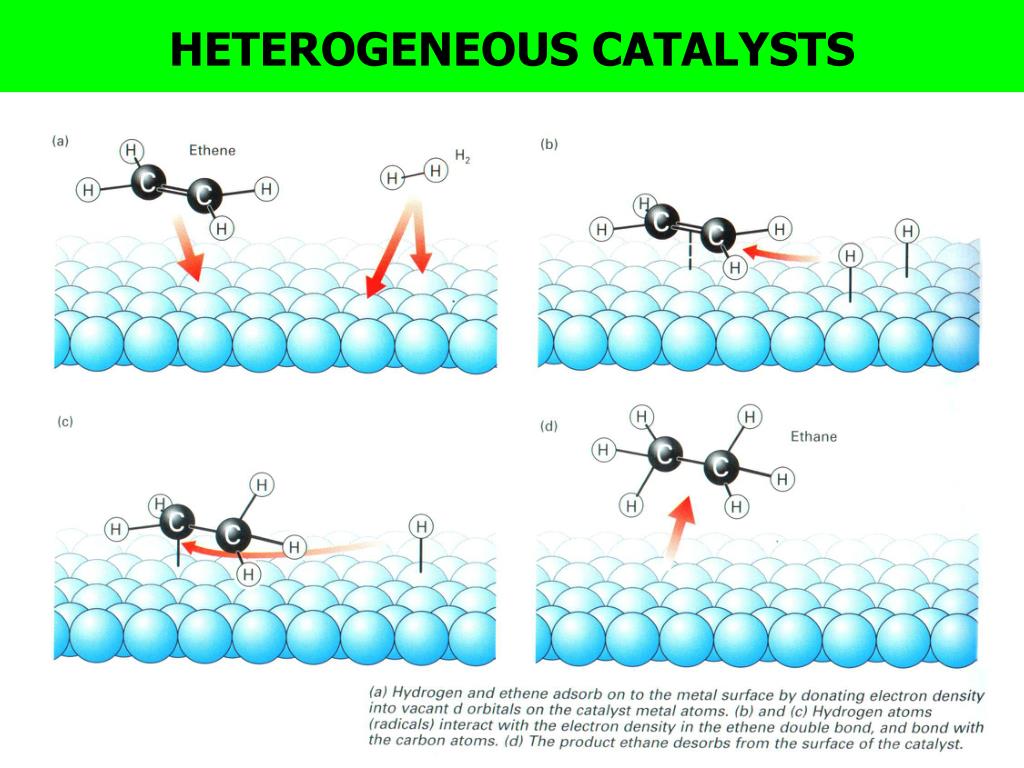



Ppt Starter 1 Definition Of Catalysts 2 Difference Between Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Catalyst Powerpoint Presentation Id




Complexities In Modeling Of Heterogeneous Catalytic Reactions Sciencedirect




Catalysis An Integrated Textbook For Students Wiley



Catalytic Mechanisms Of Hydrogen Evolution With Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Catalysts Energy Environmental Science Rsc Publishing




What Is The Difference Between Heterogeneous And Homogeneous Catalysts




Differences Between Homogeneous Catalysis And Heterogeneous Catalysis Qs Study




Catalyst Fundamentals




Preparation Of Heterogeneous Catalyst Ppt Video Online Download
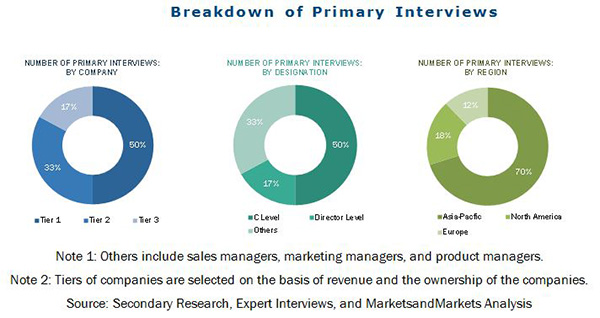



Industrial Catalyst Market By Type Region Global Forecast Marketsandmarkets Last Updated On August 21
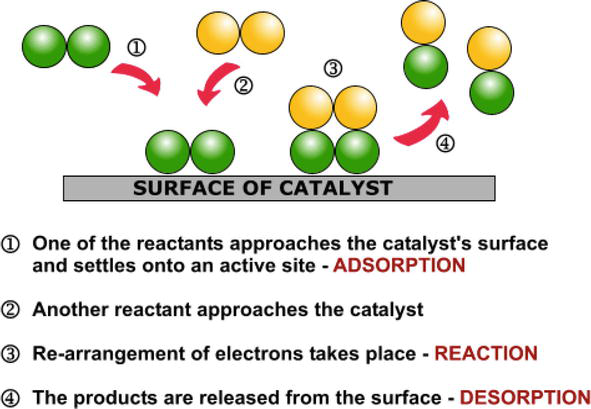



Heterogeneous Catalytic Process For Wastewater Treatment Intechopen




Catalysis Wikipedia




Heterogeneous Catalyst Discovery Using 21st Century Tools A Tutorial Rsc Advances Rsc Publishing
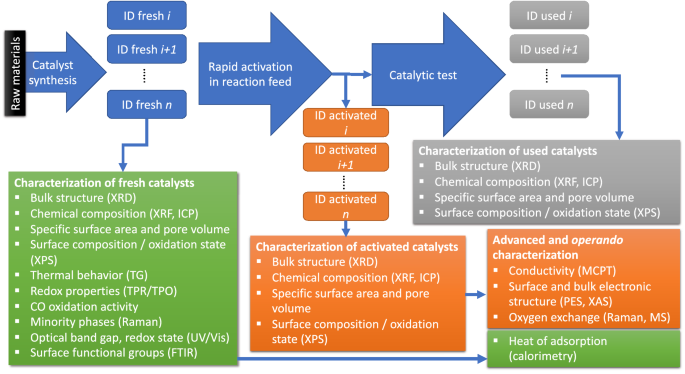



Towards Experimental Handbooks In Catalysis Springerlink




Homogeneous Catalyst An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
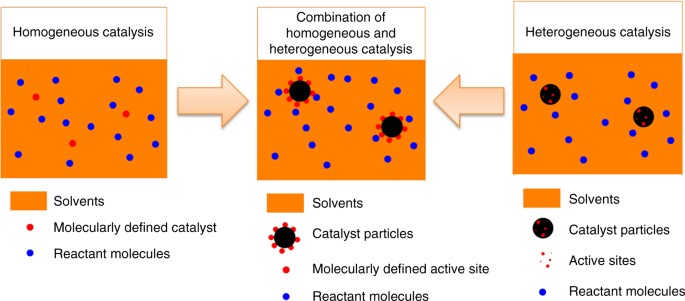



Synthesis Of A Molecularly Defined Single Active Site Heterogeneous Catalyst For Selective Oxidation Of N Heterocycles Nature Communications
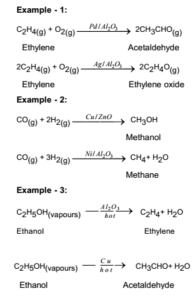



Catalysis Meaning Of Catalyst Its Characteristics And Types



1 An Introduction To Types Of Catalysis Chemistry Libretexts



Types Of Catalysts Article Kinetics Khan Academy




Heterogeneous Catalysis With Renewed Attention Principles Theories And Concepts Journal Of Chemical Education




Pdf Major Advances And Challenges In Heterogeneous Catalysis For Environmental Applications A Review
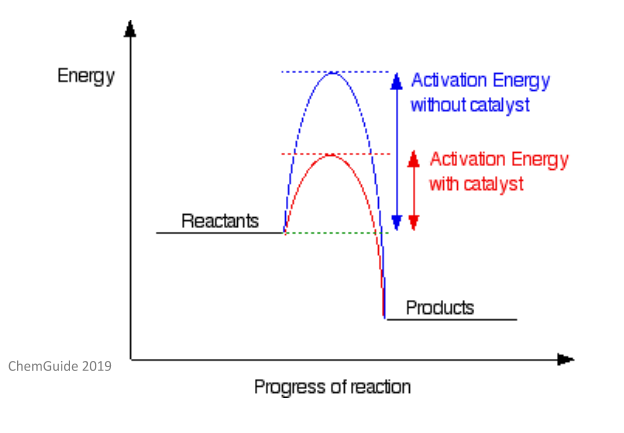



Catalyst Facts Summary Definition Chemistry Revision




Catalysis Powerpoint Slides



23 5 Features Of Homogeneous Catalysis A Catalyst




Adsorption Theory Of Heterogeneous Catalysis Youtube




Adsorption Theory Of Heterogeneous Catalyst Definition Examples




Difference Between Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Catalyst Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms




Molecular Catalysis Science Perspective On Unifying The Fields Of Catalysis Pnas




Difference Between Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Catalyst Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms



Heterogeneous Catalysis Wikipedia




Heterogeneous Catalysis Ppt Video Online Download
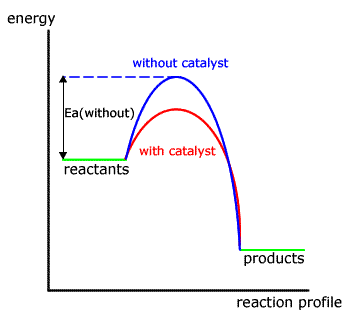



Kinetics 6 25 Catalysts
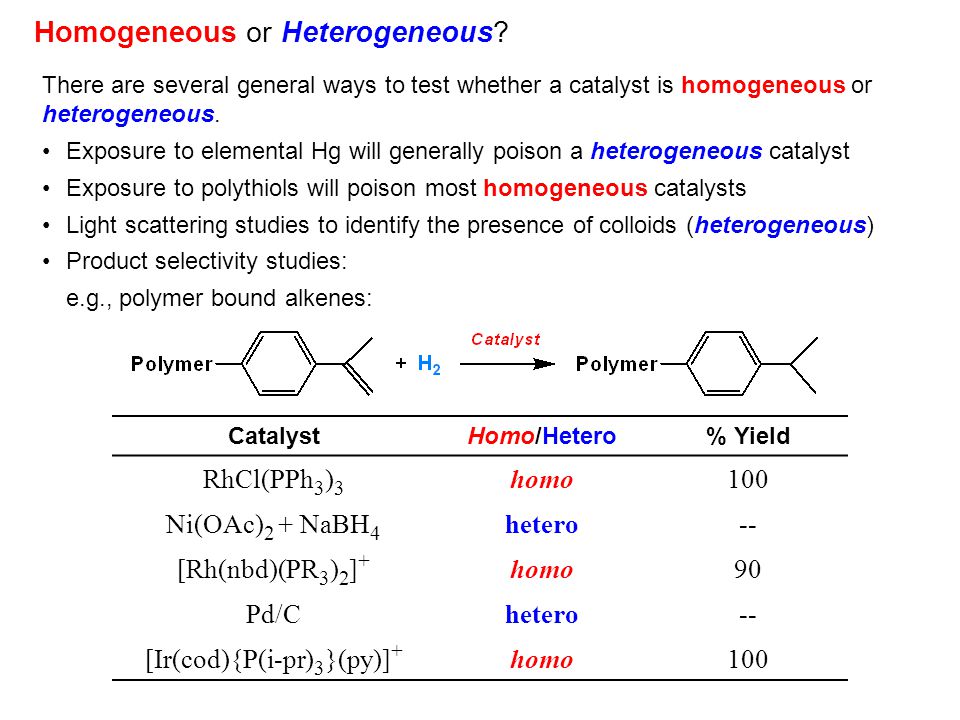



Homogeneous Catalysis Introduction Ppt Video Online Download



Q Tbn And9gctrvbbisy7ikjyh35 8msk3jkudkzizuszlwrim5fn3f2i54ygk Usqp Cau
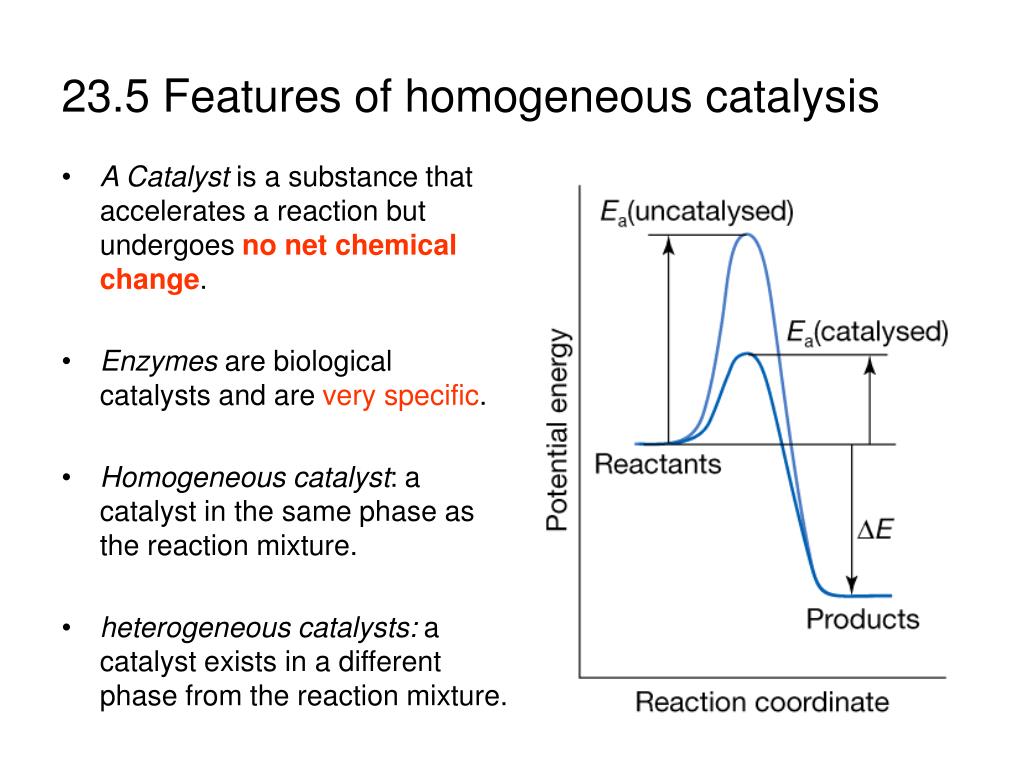



Ppt 23 5 Features Of Homogeneous Catalysis Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
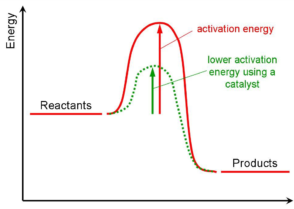



Catalysis Meaning Of Catalyst Its Characteristics And Types




Heterogenous Catalysis Chemistry Is Love




Catalysis Boundless Chemistry




Lectures 23 And 24 Chemists And Chemical Engineers Make The




Ppt Starter 1 Definition Of Catalysts 2 Difference Between Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Catalyst Powerpoint Presentation Id
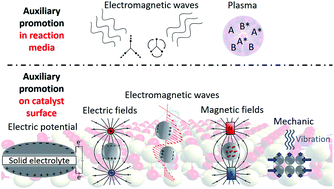



Promoting Heterogeneous Catalysis Beyond Catalyst Design Chemical Science Rsc Publishing




Catalysis Study Material For Iit Jee Askiitians



Homogeneous Vs Heterogeneous Catalysts Basic Introduction Youtube




What Is Heterogeneous Catalysis Give An Example




Pdf Heterogeneous Catalysis By Metals



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿