
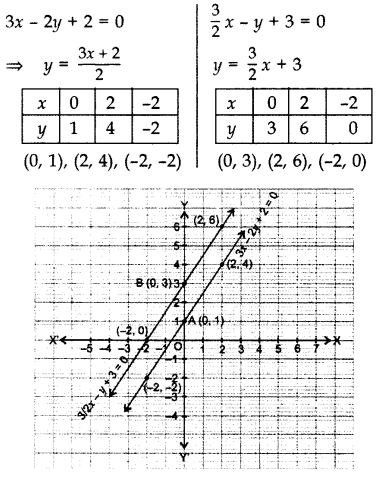
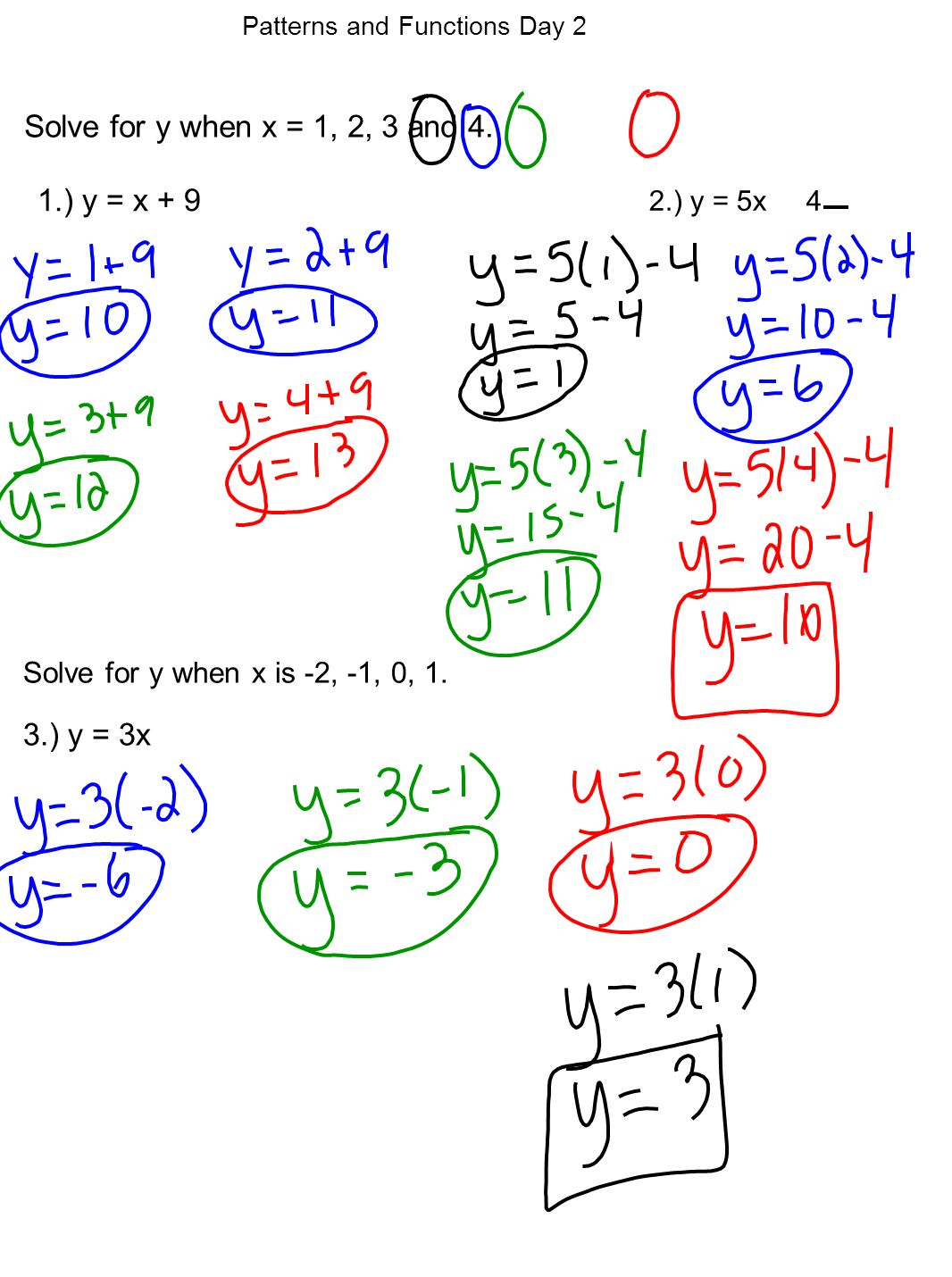
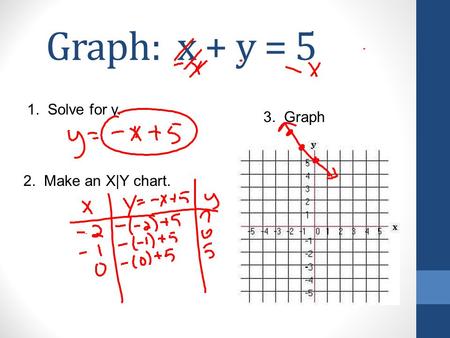
5 X 3 Y 1 3 2x 2 3y 5 Brainly In
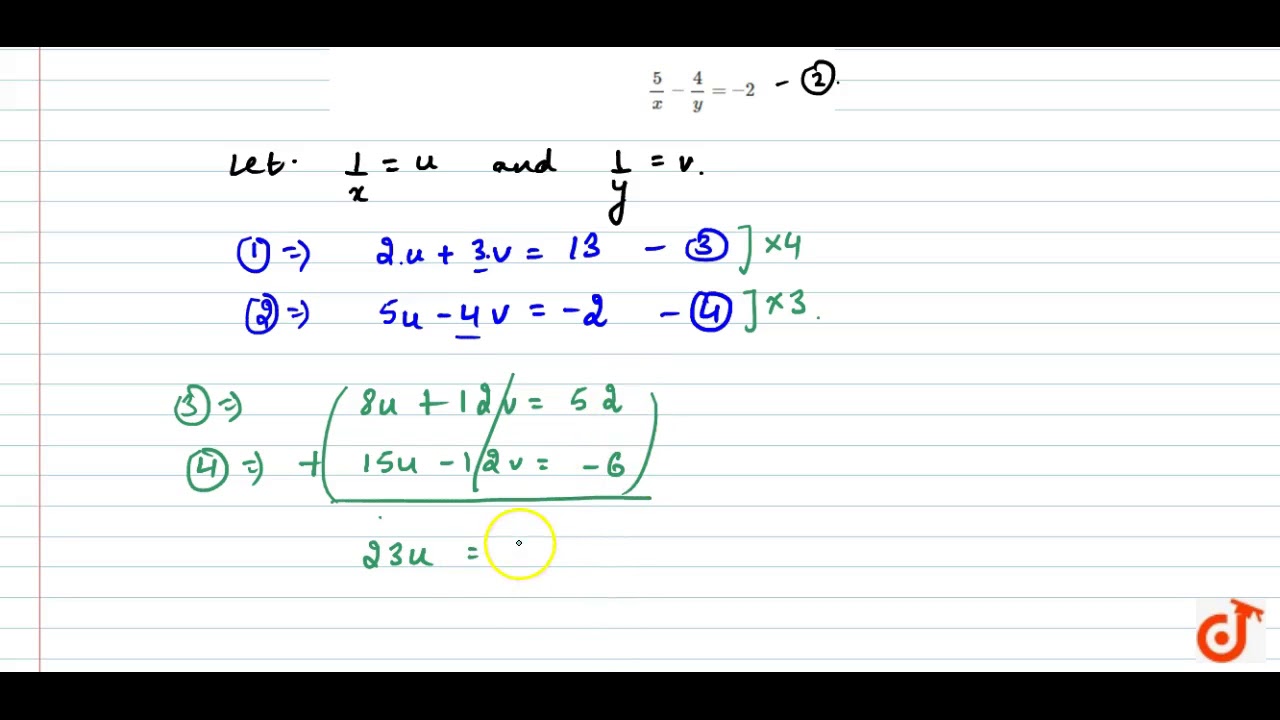
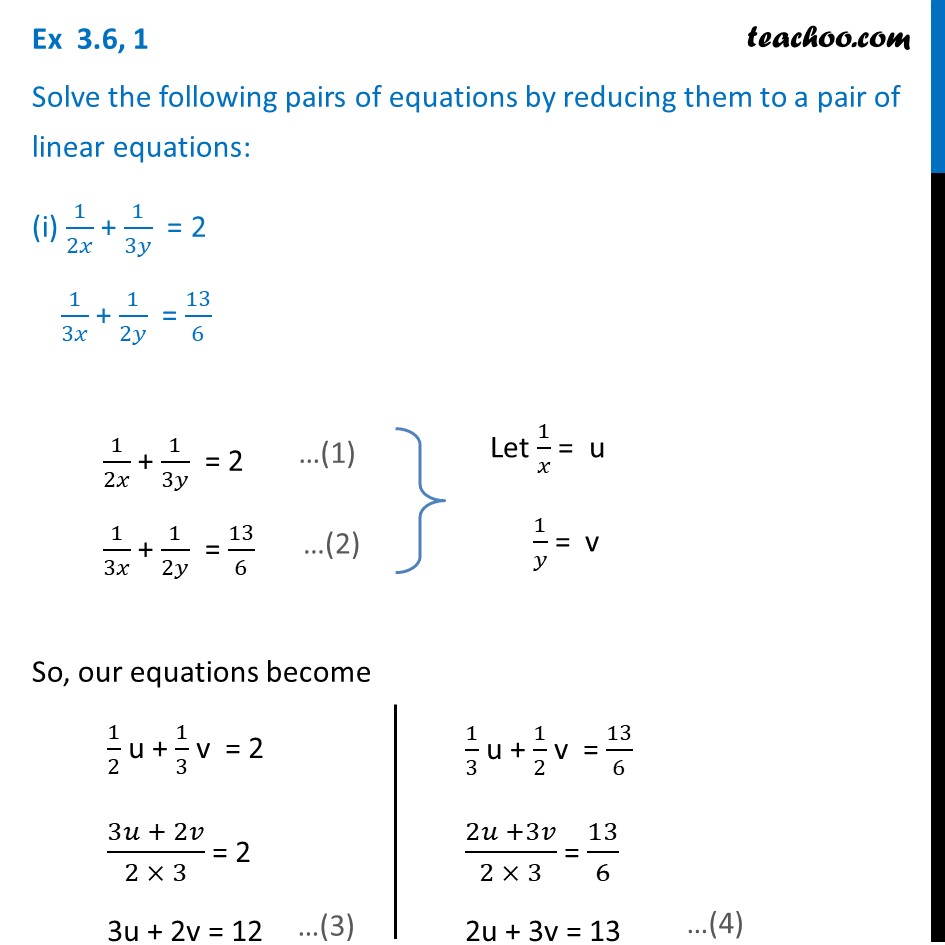
Proof lnexy = xy = lnex lney = ln(ex ·ey) Since lnx is onetoone, then exy = ex ·ey 1 = e0 = ex(−x) = ex ·e−x ⇒ e−x = 1 ex ex−y = ex(−y) = ex ·e−y = ex 1 ey ex ey • For r = m ∈ N, emx = e z }m { x···x = z }m { ex ···ex = (ex)m • For r = 1 n, n ∈ N and n 6= 0, ex = e n n x = e 1 nx n ⇒ e n x = (ex) 1 • For r rational, let r = m n, m, n ∈ N5/x11/y2=2 6/x13/y2 by reducing to a pair of linear equation Other questions on the subject Mathematics Mathematics, 1430, meramera50 Find the arc length parameter along the given curve from the point where tequals=0 by evaluating the
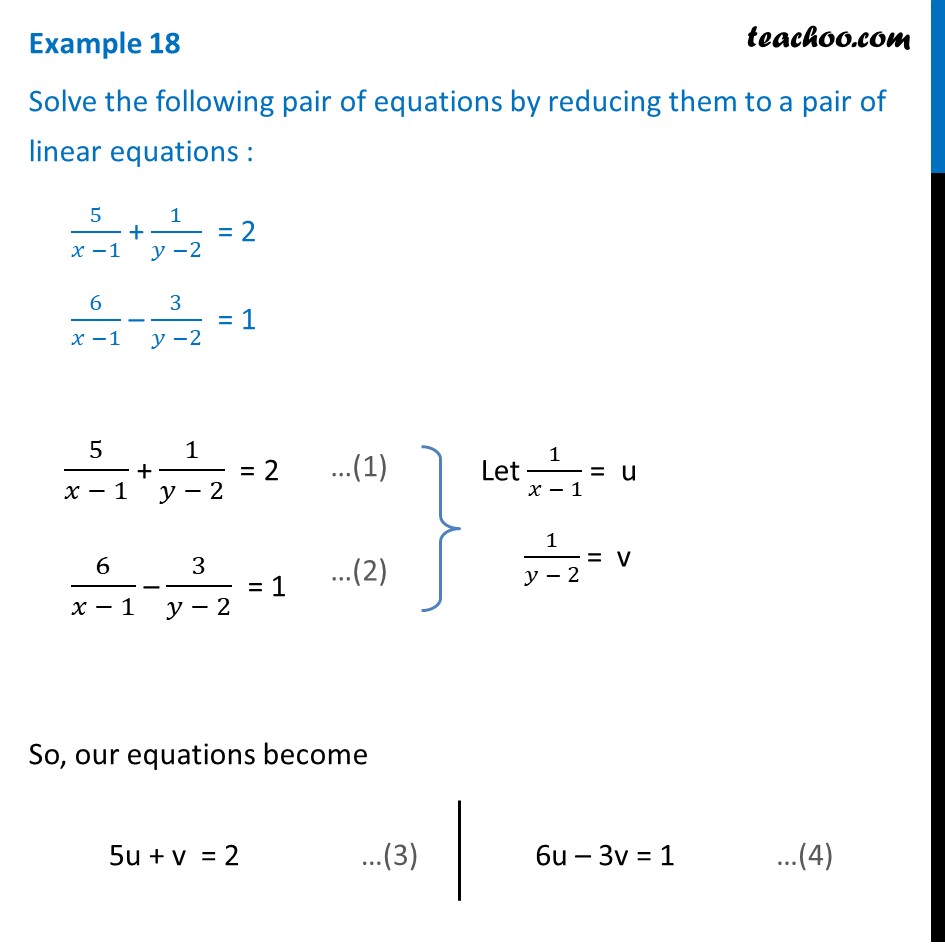
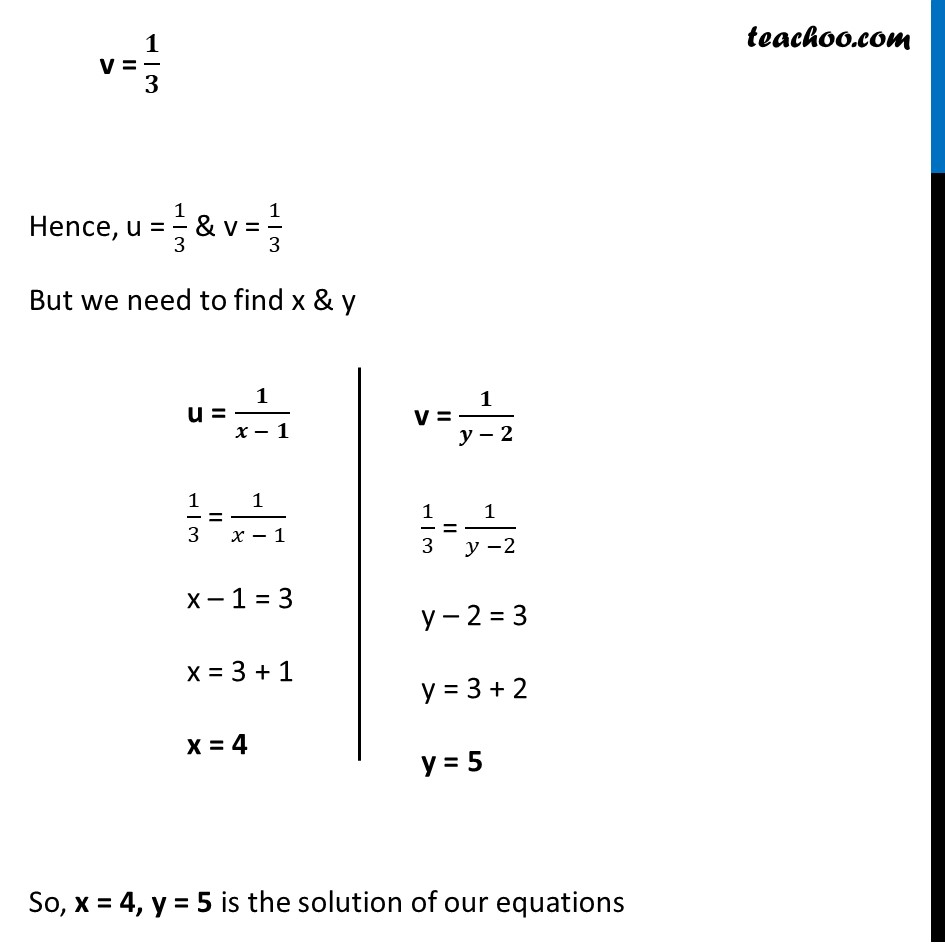
5/x-1 1/y-2=2 6/x-1-3/y-2=1 by reducing method
5/x-1 1/y-2=2 6/x-1-3/y-2=1 by reducing method-Homework 2 Solutions Igor Yanovsky (Math 151B TA) Section 53, Problem 1(b) Use Taylor's method of order two to approximate the solution for the following initialvalue problem( frac{5}{x1}frac{1}{y2}=2dots left(iright))( frac{6}{x1}frac{3}{y2}=1dots left(iiright))Let( frac{1}{x1}=P,frac{1}{y2}=Q)Putting in ( left(iright)) and

Solve The Equations 5x 1 1y 2 2 And 6x 1 3y 2 1
Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with stepbystep explanations, just like a math tutorAnswer (1 of 8) First, remember that your ultimate goal in solving this equation will be to isolate the variable X by itself on one side of the equation First, distribute the 2 on the left side 2(X1)=5–2X 2x2=5–2x Add 2x to both sides;5/x11/y2=2;6/x13/y2=1, solve this equation by substituting method
R has the form f(x) = a ¢ x2Generalization of this notion to two variables is the quadratic form Q(x1;x2) = a11x 2 1 a12x1x2 a21x2x1 a22x 2 2 Here each term hasThis will cancel out the 2x on the right side 4x2=5Algebra Calculator is a calculator that gives stepbystep help on algebra problems See More Examples » x3=5 1/3 1/4 y=x^21 Disclaimer This calculator is not perfect Please use at your own risk, and please alert us if something isn't working Thank you
5/x-1 1/y-2=2 6/x-1-3/y-2=1 by reducing methodのギャラリー
各画像をクリックすると、ダウンロードまたは拡大表示できます
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 | 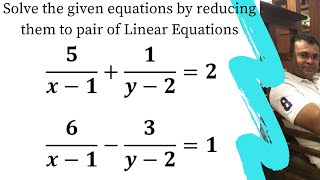 | |
「5/x-1 1/y-2=2 6/x-1-3/y-2=1 by reducing method」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  |  |
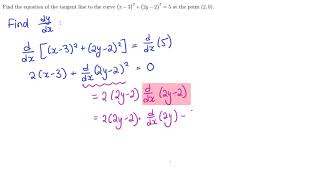 |  | |
「5/x-1 1/y-2=2 6/x-1-3/y-2=1 by reducing method」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  | |
 | ||
「5/x-1 1/y-2=2 6/x-1-3/y-2=1 by reducing method」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  | |
 |  | |
「5/x-1 1/y-2=2 6/x-1-3/y-2=1 by reducing method」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 | ||
 |  |  |
「5/x-1 1/y-2=2 6/x-1-3/y-2=1 by reducing method」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
 | ||
 |  | |
「5/x-1 1/y-2=2 6/x-1-3/y-2=1 by reducing method」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | 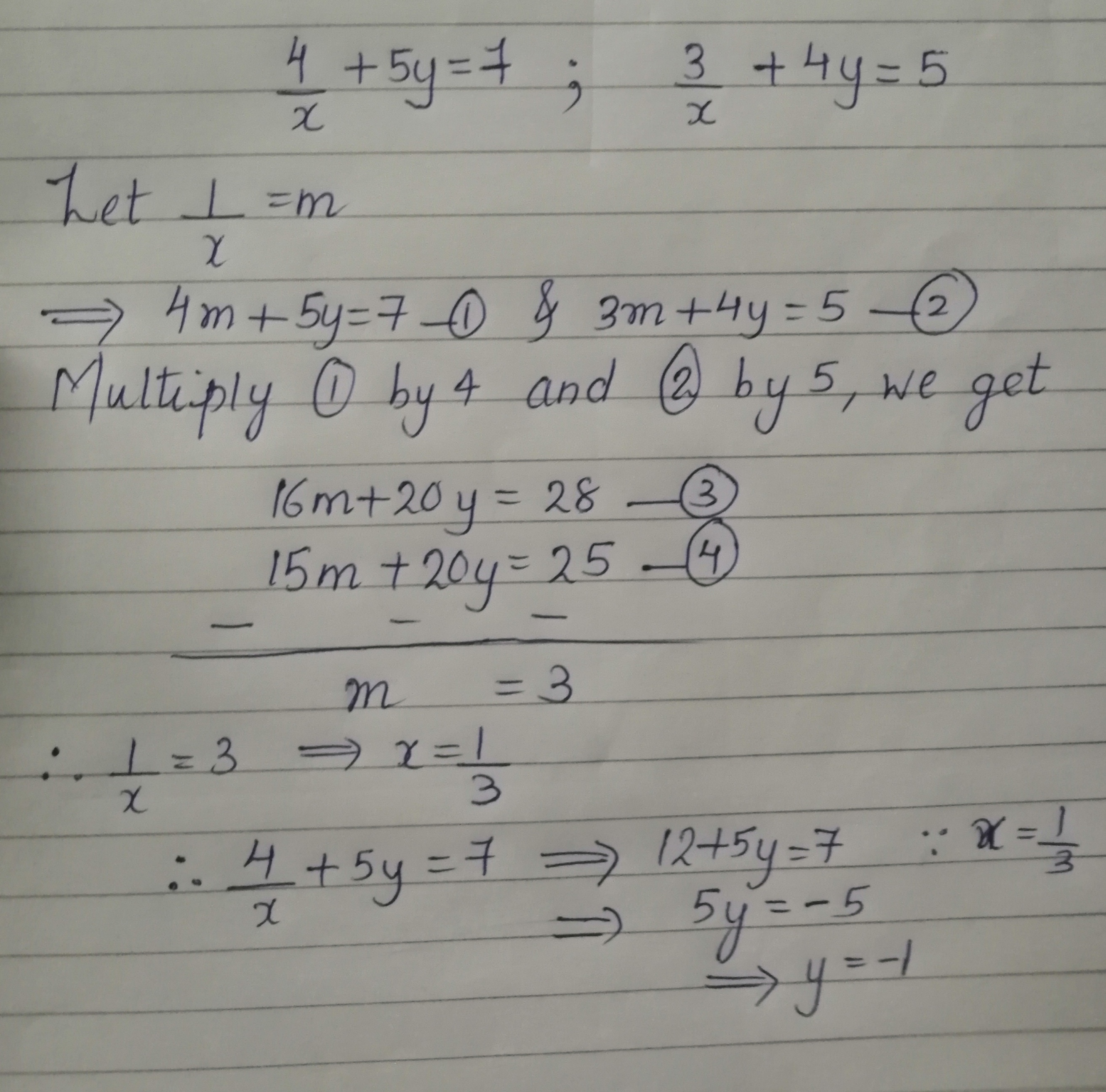 | |
 | 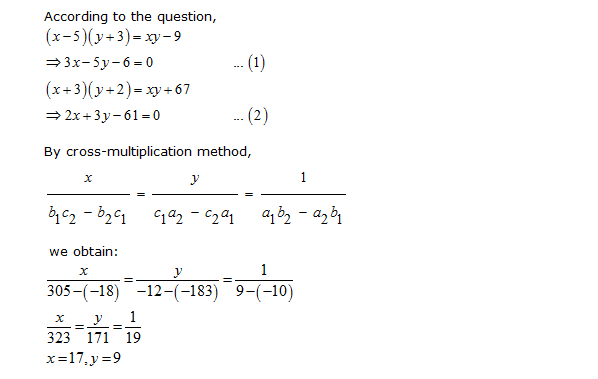 |  |
 |  | |
「5/x-1 1/y-2=2 6/x-1-3/y-2=1 by reducing method」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「5/x-1 1/y-2=2 6/x-1-3/y-2=1 by reducing method」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「5/x-1 1/y-2=2 6/x-1-3/y-2=1 by reducing method」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
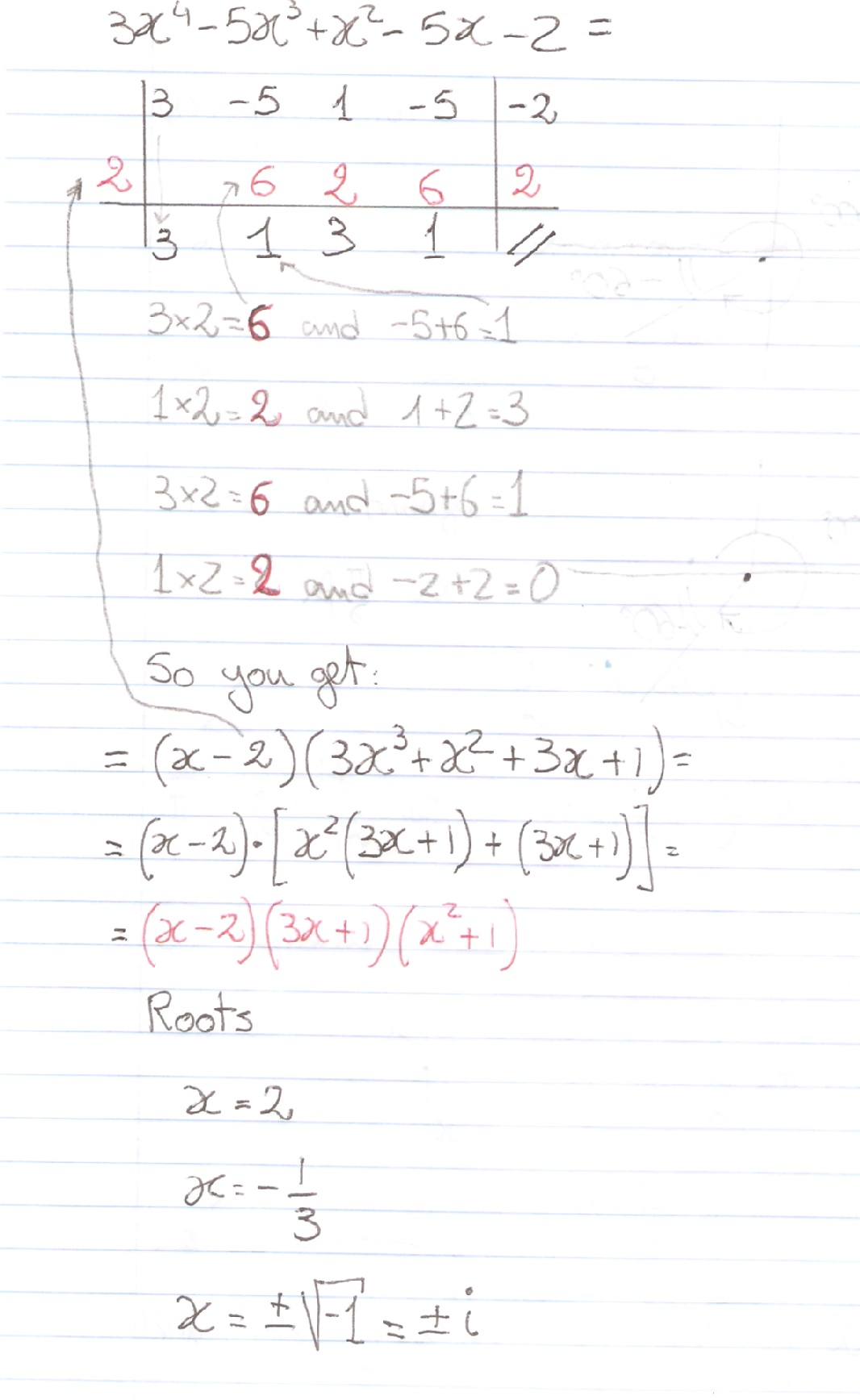 | ||
「5/x-1 1/y-2=2 6/x-1-3/y-2=1 by reducing method」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  | |
 | ||
「5/x-1 1/y-2=2 6/x-1-3/y-2=1 by reducing method」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  |
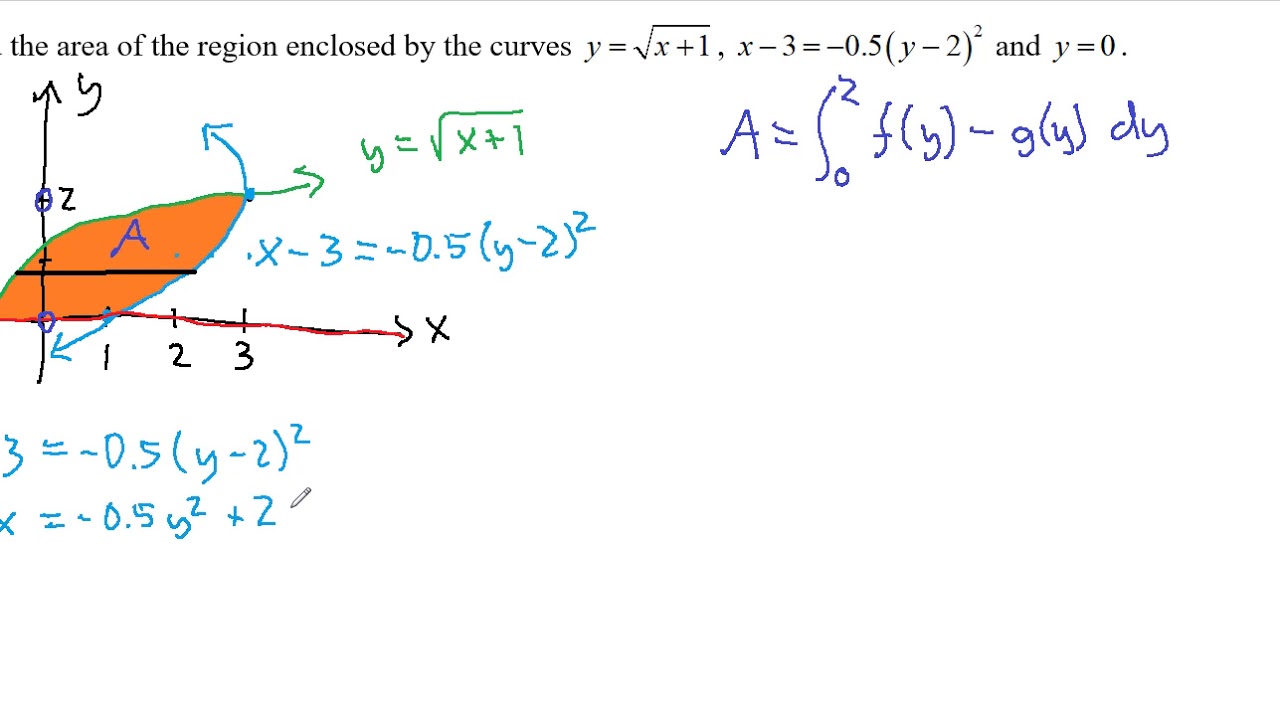
Y=4 y=4 y=l 3 x 0 2 1 Y x 1 r=2 Fig 143 Thin sticks above and below (Example 2) Reversed order (Examples 3 and 4) 141 Double Integrals EXAMPLE 4 Reverse the order of integration in Solution Draw a figure!EduRev Class 10 Question is disucussed on EduRev Study Group by 114 Class 10 Students





0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿